Adaboost Using Decision Stump
Adaboost algorithm implementation using Decision Stumps as weak learners to classify a dataset with improved accuracy.
Title: Adaboost Using Decision Stump
Description: Adaboost algorithm implementation using Decision Stumps as weak learners to classify a dataset with improved accuracy.
Source code link: https://github.com/ompranavagrawal/AdaboostUsingDecisionStump.git
Objective
The goal is to implement the Adaboost algorithm using Decision Stumps as weak learners to classify a dataset with improved accuracy. Decision Stumps are one-level Decision Trees that use a single attribute to make a decision, making them perfect for use as weak learners in the Adaboost algorithm.
Implementation Details
Dataset Preparation
The dataset is first preprocessed to ensure it is suitable for training and testing the Adaboost model. This involves cleaning, normalization (if necessary), and splitting the dataset into training and testing sets.
Decision Stump as Weak Learner
- Decision Stump Implementation: Each decision stump is implemented to select the best threshold for splitting the data based on the Gini Index. This involves evaluating every feature in the dataset to determine the best split.
- Feature Selection: The algorithm iteratively considers each feature in the dataset, calculating the Gini Index for different splitting points to find the feature and threshold that provide the best split.
Adaboost Algorithm
- Initialization: Initialize weights for each instance in the dataset equally.
- For each iteration::
- Train a decision stump using the current weights.
- Calculate the stump's error rate: The error is measured based on how well the stump performs on the weighted dataset.
- Compute the stump's weight in the final classification: This is based on the stump's error rate, with more accurate stumps receiving higher weights.
- Update weights for each instance: Increase weights for incorrectly classified instances and decrease for correctly classified ones, ensuring that subsequent stumps focus more on difficult cases.
- Normalize weights to ensure they sum up to 1.
- Final Model: Combine the decision stumps into a weighted sum that represents the final model.
Parameter Tuning
The number of decision stumps is a critical parameter. The implementation tests the performance of the Adaboost model with a varying number of stumps to find the optimal count that minimizes error without leading to overfitting.
Results and Observations
The implementation showcased that as the number of decision stumps increased, the model's ability to classify the training data improved, with diminishing returns and eventual overfitting beyond an optimal point. This optimal range of stumps provided the best balance between bias and variance, leading to improved generalization on unseen data compared to a single decision tree.
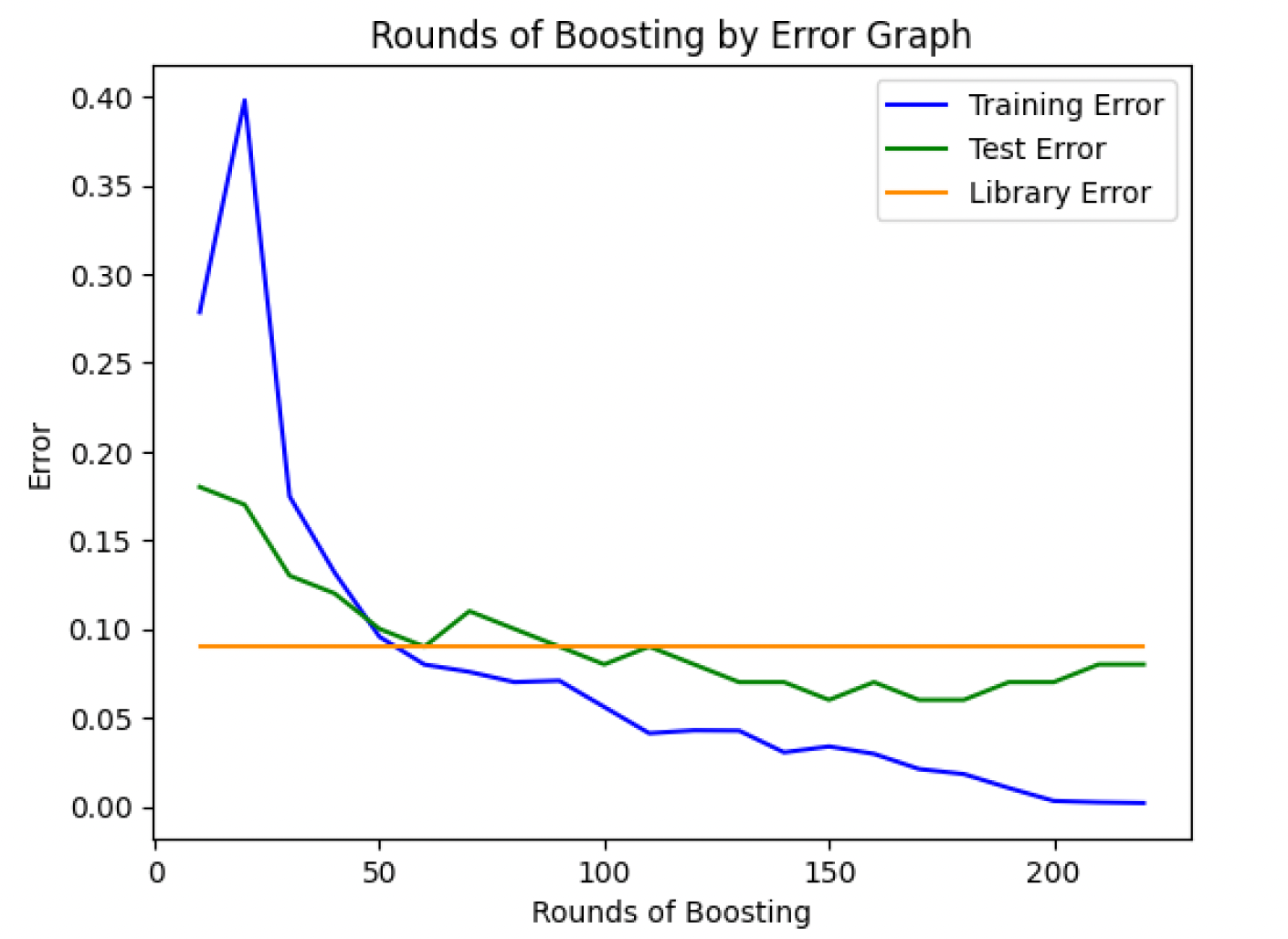
Boosting vs Error Graph
Conclusion
The implementation of the Adaboost algorithm using Decision Stumps as weak learners demonstrated significant improvements in prediction accuracy over a baseline decision tree model. By carefully tuning the number of stumps, it is possible to achieve a robust model that generalizes well to new data, showcasing the power of ensemble learning techniques in machine learning.